8/6/19 · Relative risk is used in randomized controlled trials and cohort studies Relative Risk is calculated by dividing the probability of an event occurring for group1 divided by the probability of an event occurring for group2 Relative Risk is very similar to Odds Ratio, however, RR is calculated by using percentages, whereas the Odds Ratio isI don't think it > would be reasonable to refer to the ratio of any two > probabilities as a "relative risk" > > David > > Original Message > From n p mailtonik_padazis@yahoocom > Sent 03 June 05 1013 > To statalist@hsphsun2harvardedu > Subject Re st odds ratio vs RRR in multinomial > logistic regression > > > Suppose your dependent variable Y has three >10/1/13 · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size

How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
Which is better odds ratio or relative risk
Which is better odds ratio or relative risk-15/5/14 · The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio May 15, 14 • ericminikel The other day I was emailing with a statistical genetics colleague about a rare SNP associated with a phenotype I stated that the minor allele frequency (MAF) was 07% in cases and 01% in controls, for a risk ratio of 7 After clicking send, I felt a twinge of regretFor estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithm We can specify this manually, or just use a builtin family for our generalized linear model for which the logarithm is the canonical link fucntion, and hence the default



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table
1/10/07 · Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds ratioThis is not true for relative risk Switching the rows or columns inverts the odds ratio For example, the odds ratio for no cough given a history of bronchitis = (247/26)/(1002/44) = 0417 = 1/2397 This is the reciprocal of the OR for cough There are only two possible odds ratios, as switching both rows and columns gives
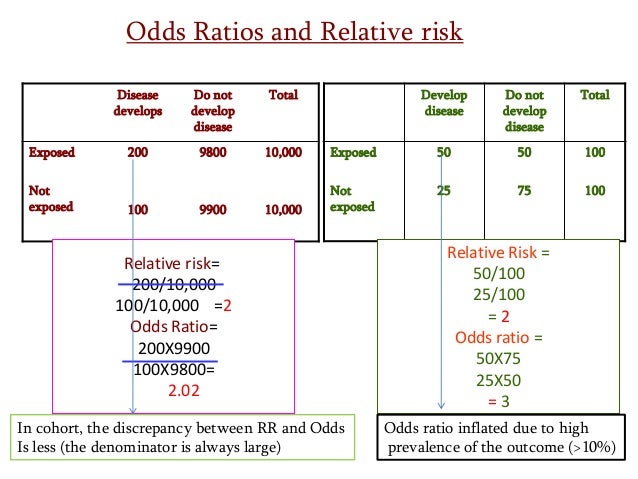
Palabras clave Odds ratio, Riesgo relativo SUMMARY The odds ratio (OR) and relative risk (RR) are measures of association for dichotomous nominal variables The OR has been widely used for biomedical research, the reasons for this are 1) The OR determines an estimate (with confidence interval) for relations between binary dummyThe relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative riskThe absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group
In practice the odds ratio is commonly used for casecontrol studies, as the relative risk cannot be estimated In fact, the odds ratio has much more common use in statistics, since logistic regression, often associated with clinical trials, works with the log of the odds ratio, not relative risk9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effectsOdds Ratio, Relative Risk, and Risk Difference How to Use Odds Ratio, Relative Risk, and Risk Difference to Describe the Association Between Two Categorical



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios


Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink
Relative risk, Risk difference and Odds ratio When the data to be analyzed consist of counts in a crossclassification of two groups (or conditions) and two outcomes, the data can be represented in a fourfold table as follows17/2/21 · For example, a relative risk of 15 would suggest a 50% increase in risk, whereas a relative risk of 05 would suggest a 50% decrease in risk Odds ratios The main difference between this and the other two measures is that there is no way of including a time element in this model2/9/ · The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard)



Glossary Of Research Terminology



Wasp Write A Scientific Paper Using Excel 12 Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Sciencedirect
6/4/10 · RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Risk and Odds just seemed the same to me for a long time Since then, I have come to understand to important difference Lets start with Relative Risk Relative Risk can be addressed by asking the following question How many times more likely is an "exposed" group to develop aOdds Ratio = Odds / Odds Now that you have a general idea of what odds ratio and relative risk are you need to know when to use them They don't always just ask you to calculate one or the other Sometimes questions on Step 1 also require you to figure out which type of calculation is needed based on the situation In clinical trials andOdds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiert


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data


Epidemiology Stepwards
· Odds ratio (OR), risk ratio (RR), and prevalence ratio (PR) are some of the measures of association which are often reported in research studies quantifying the relationship between an independent variable and the outcome of interest There has been much debate on the issue of which measure is appropriate to report depending on the study designRelative Risk vs Odds ratio Relative Risk vs Odds ratio Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device8/1/16 · You may have noticed that the odds ratio and relative risk are very similar in this case This happens when the proportions being compared are both close to 0 Which one you decide to use is a matter of personal preference and perhaps your audience



Bi Practice Page 4 A Journey Of A Thousand Miles Begins With The First Step



Related Image Cross Sectional Study Odds Intervention
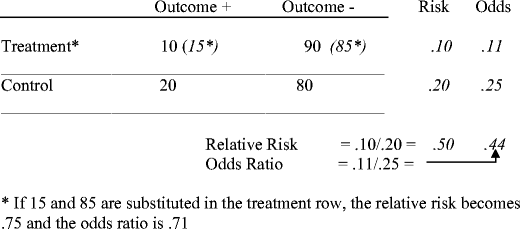
Risk = odds/(1odds) "Most published research providing an odds ratio as a measure of effect size should also provide sufficient information for the baseline risk, and hence the relative risk, to be calculated If numbers in each group are given, the crude relative risk can be calculated directly" – BMJ 14;348f7450 doi /bmjf7450The simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variableBoth the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio Finally, the odds ratio avoids ambiguity by being invariant to lthe labeling



Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj


Estimating Risk
In the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measuresA prevalence ratio, or ;7/2/14 · c) The odds ratio is an estimate of the population relative risk d) The odds ratio is a measure of the strength of the association between the intervention and antibiotic associated diarrhoea compared with placebo



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Math3010 Week 6
The odds ratio and the relative risk will not always disagree by this much Large effects on groups with high initial risk seem to cause the most problems See Davies et al (1998) for some useful guidelines for when the odds ratio and relative risk are likely to differ When they do differ, the relative risk represents the typical interpretationRelative risk refers to a ratio between members of the population expressing the trait of interest (eg cancer), with distinction made between whether or not those members had previously been exposed to a related risk Odds Ratio (OR) Odds ratios refer to a ratio between members within a population expressing aThere can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ;


Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download


How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy
Portantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998) And it is this fact that enables us, most of the time, to approximate the relative risk with the odds ratio Table 5 below illustrates the relationship between RR and OR for some probabilities of the outcomeThe odds ratio is a useful measure of association for a variety of study designs For a retrospective design called a casecontrol study, the odds ratio can be used to estimate the relative risk when the probability of positive response is small (Agresti 02)In a casecontrol study, two independent samples are identified based on a binary (yesno) response variable, and the conditional1/6/09 · RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ;



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Of Death According To Biomarkers Of Risk Download Scientific Diagram



Phg301 Hw Win19 Flashcards Quizlet
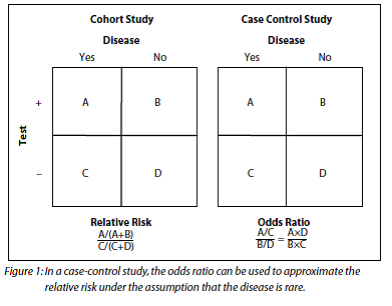
Relative risk and odds ratio The relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a populationThus the odds ratio is (a/b) / (c/d) which simplifies to ad/bc This is compared to the relative risk which is (a / (ab)) / (c / (cd)) If the disease condition (event) is rare, then the odds ratio and relative risk may be comparable, but the odds ratio will overestimate the risk ifA rate ratio, ;



Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect
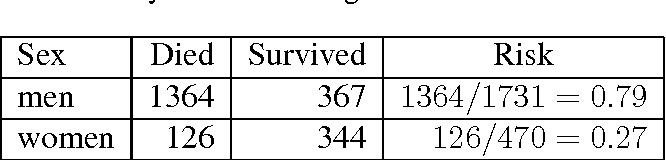


Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar
16/9/02 · Cases 1 and 4 have the same absolute risk reduction, NNT, and odds ratios, but very different relative risk, relative risk reduction, and risk at baseline Real Example The following example 18 is a prospective study, which compares the incidences of dyskinesia after ropinirole (ROP) or levodopa (LD) in patients with early Parkinson's disease7/8/14 · If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept The odds indicates how much more likely is an event to occur than not to occur (p/(1p))11/7/16 · The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio


Diminishing Odds Ratios Published In Pubmed Health Geomatics Lab
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)16/8/18 · For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean);26/8/ · Table 1 Relative risk (RR) vs Odds Ratio (OR) vs Hazard Ratio (HR) HRs are in tandem with survivorship curves, which show the temporal progression of some event within a group, whether that event is death, or contracting a disease



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
1/2/08 · Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeable28/3/1998 · Odds ratios are a common measure of the size of an effect and may be reported in casecontrol studies, cohort studies, or clinical trials Increasingly, they are also used to report the findings from systematic reviews and metaanalyses Odds ratios are hard to comprehend directly and are usually interpreted as being equivalent to the relative risk19/3/18 · How to Interpret Risk Ratios Since the relative risk is a simple ratio, errors tend to occur when the terms "more" or "less" are used Because it is a ratio and expresses how many times more probable the outcome is in the exposed group, the simplest solution is to incorporate the words "times the risk" or "times as high as" in your interpretation



Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk 63 Table 5 Examples Of Rr And Or For Different Probabilities ˇ 1 ˇ 2 Rr Or 4 1 4 6 2 3 67 58 04 Pdf Document
1/6/00 · ODDS RATIOS and relative risks are commonly used to express results in clinical studies The results of cohort studies and casecontrol studies are best expressed as relative risks and odds ratios, respectively The use and interpretation of these ratiosThe odds ratio (OR) is a ratio of 2 numbers, like the relative risk we have 3 options OR = 1 The odds in the first group are the same as those in the second So no evidence that drinking wine can either OR > 1 The odds of having the disease in the exposed group are higher than the unexposedEven an odds ratio;


Risk Differences Odds Ratios And Relative Risks Plots With Proc Freq



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Ci For Or And Rr Relative Risk Odds Ratio



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube



Pdf Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk For Cross Sectional Data Semantic Scholar



Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk


Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream



How To Calculate Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Google Search Case Control Study Cancer Patients Central Nervous System



Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08


Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper


Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International



Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio


Relative Risk Odds Ratio



Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
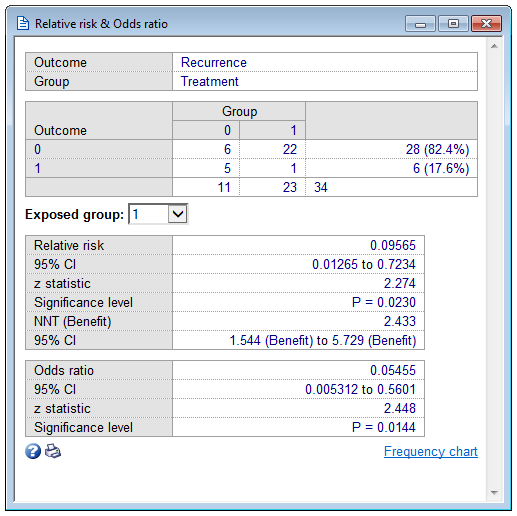


Relative Risk Odds Ratio


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data


Relative Risk Wikipedia



Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table
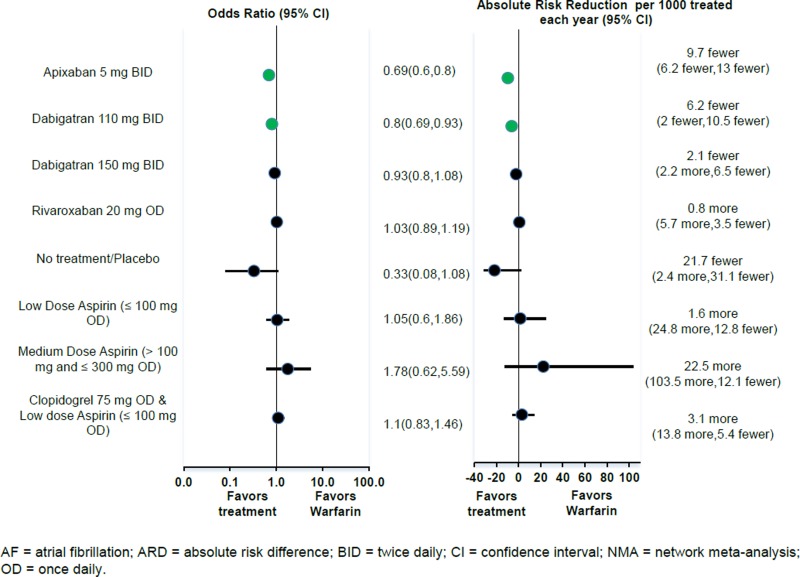


Figure 3 Odds Ratio And Absolute Risk Difference Of Major Bleeding For Antithrombotic Therapies Relative To Adjusted Dose Warfarin For Patients With Af Fixed Effects Nma Antithrombotic Agents For The Prevention Of Stroke



Literature Search


Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream



Measuring Of Risk



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Relative And Attributable Risks Absolute Risk Involves People



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia



Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk



Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download



Understanding The Odds Ratio And The Relative Risk Simon 01 Journal Of Andrology Wiley Online Library



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney



Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Relative Risk Wikipedia



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
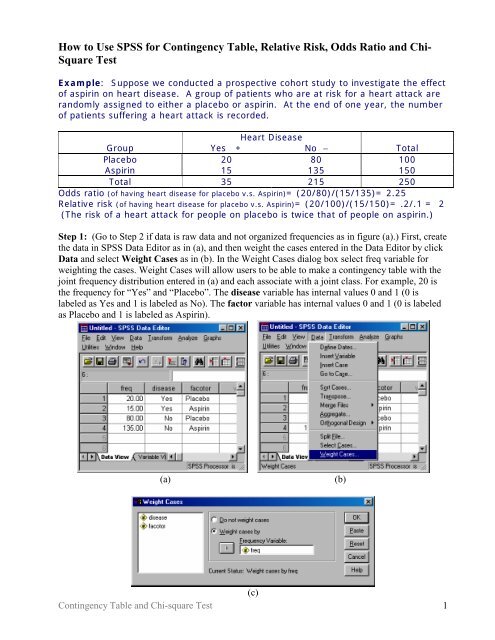


How To Use Spss For Contingency Table Relative Risk Odds Ratio



Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



Average Values Measures Of Association N Absolute Risk The Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Provide A Measure Of Risk Compared With A Standard N Attributable Ppt Download



Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk



Or2rr


Requesting Effect Measures



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Solved Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Rati Chegg Com



Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February
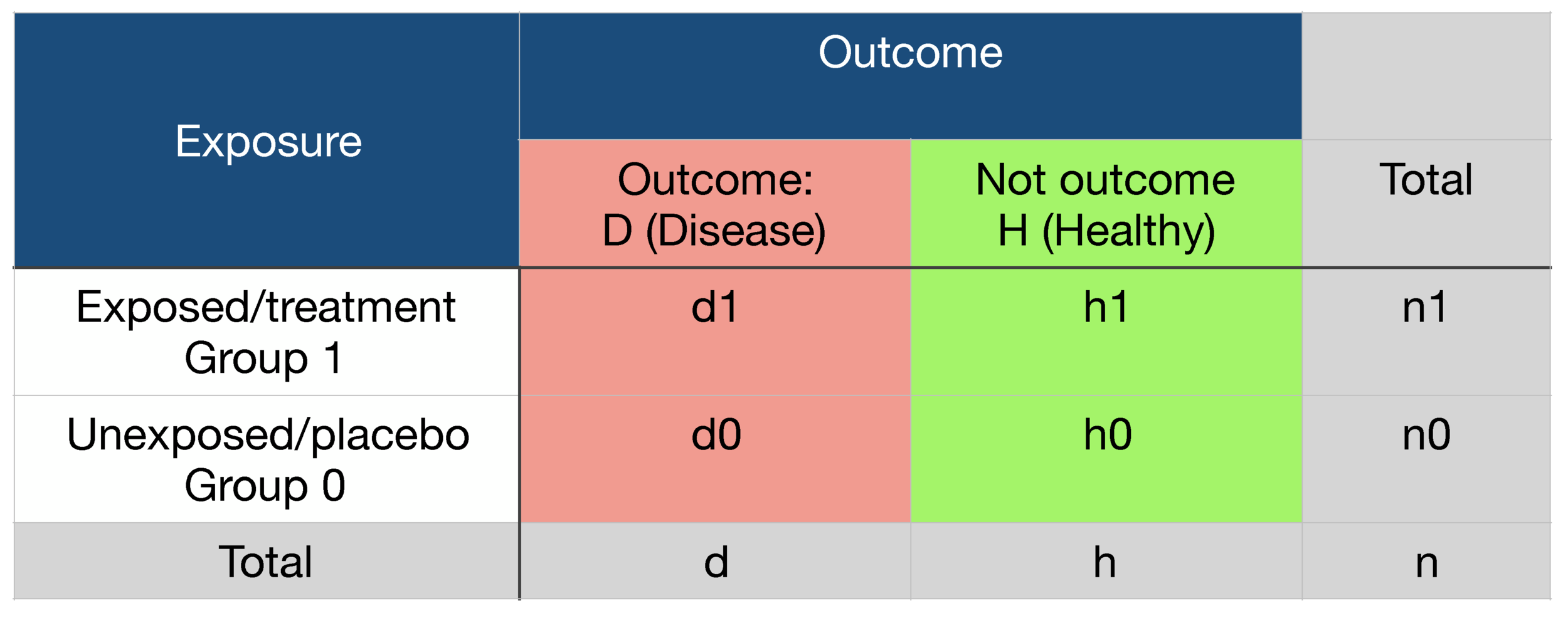


Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf
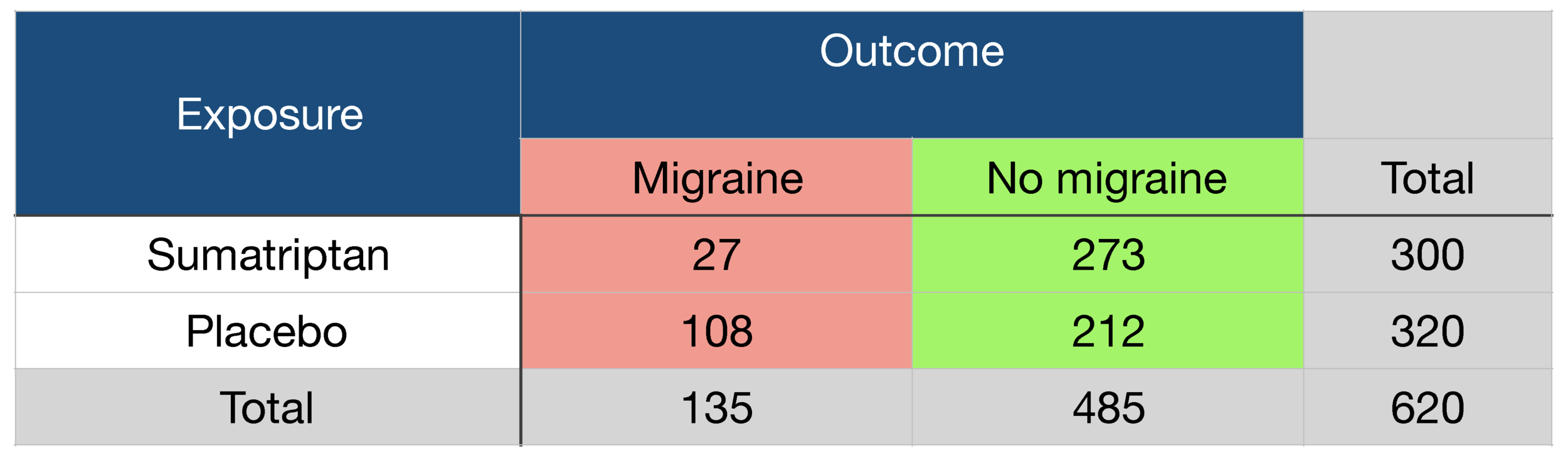


Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj


6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Relative Risks Odds Ratios John Snow S Cholera Investigations



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿